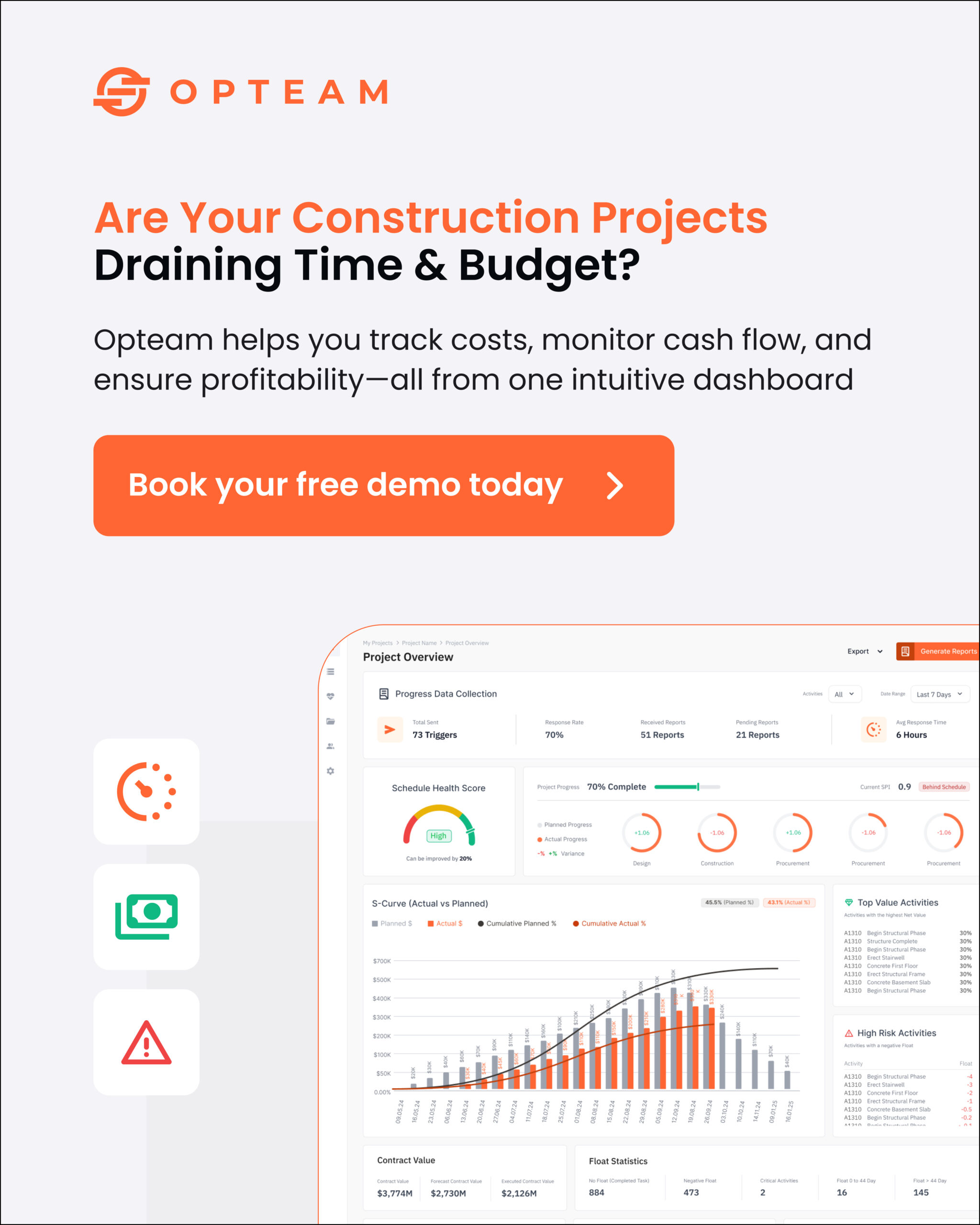
The Schedule Performance Index (SPI) is a key performance indicator in project management, used to measure the efficiency of time utilization on a project. It is calculated by dividing the Earned Value (EV) by the Planned Value (PV). SPI helps project managers understand whether a project is ahead of or behind schedule.
Schedule Performance Index (SPI) Calculator
Understanding the Schedule Performance Index (SPI)
The Schedule Performance Index (SPI) is a key metric used in project management to evaluate how efficiently time is being utilized on a project. By comparing the Earned Value (EV), which represents the value of work actually performed, to the Planned Value (PV), which represents the value of work planned to be performed, SPI provides a quantitative measure of schedule efficiency.
This index is essential for project managers to gauge whether their project is on track with the planned timeline. An SPI value of 1 indicates that the project is progressing exactly as scheduled, while an SPI value less than 1 signifies that the project is behind schedule, and a value greater than 1 suggests that the project is ahead of schedule.
Effective time management is crucial for the success of any project, making SPI a vital tool in the project manager’s toolkit. Regularly monitoring the SPI allows project managers to identify potential delays early and implement corrective actions to bring the project back on track. Additionally, it helps in making informed decisions about resource allocation, scheduling adjustments, and other strategic changes needed to ensure timely project completion. Overall, the SPI fosters better control and transparency, enabling project managers and stakeholders to achieve project goals within the stipulated timeframe.
Components of the SPI Formula
- Earned Value (EV):
- The value of work actually performed up to a specific point in time, expressed in terms of the approved budget.
- Planned Value (PV):
- The value of work planned to be performed up to a specific point in time, according to the project schedule.
SPI Formula
SPI = EV / PV
- EV: Represents the budgeted value of the work actually completed.
- PV: Represents the budgeted value of the work planned to be completed.
Interpretation of SPI
- SPI < 1: The project is behind schedule.
- SPI = 1: The project is on schedule.
- SPI > 1: The project is ahead of schedule.
Importance of SPI in Project Management
- Schedule Control:
- SPI helps in monitoring the project schedule performance and identifying if the current performance is on track.
- Performance Measurement:
- Provides a quantitative measure of the schedule efficiency, enabling better performance assessment and management.
- Decision Making:
- Assists project managers in making informed decisions regarding schedule adjustments and corrective actions to keep the project on track.
- Transparency and Accountability:
- Promotes transparency and accountability in schedule management, ensuring that project timelines are closely monitored and controlled.
Example Calculation
Suppose a project has an Earned Value (EV) of $600,000 and a Planned Value (PV) of $700,000:
SPI= 600,000 / 700,000
SPI=0.86
This indicates that the project is behind schedule, as the SPI is less than 1.
Read more: